What is a DCS System?
- Definition of DCS:
A Distributed Control System (DCS) is an automated control system that consists of a network of controllers, field devices, and human-machine interfaces (HMIs) that are distributed throughout a plant or facility. DCS systems are commonly used in large-scale industrial processes where centralized control is not feasible or efficient.
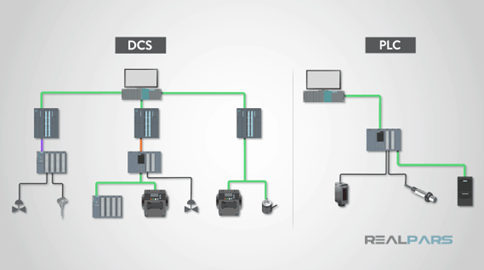
- Components of a DCS:
- Controllers: Distributed throughout the plant, these controllers manage and control different parts of the process. Each controller typically handles a specific section or unit of the process.
- Field Devices: Sensors, actuators, and other devices that interface with the physical processes, providing data to the controllers and executing control commands.
- HMI: The interface through which operators interact with the system. It provides visualization of the process, control capabilities, and alarm management.
- Communication Network: The backbone of a DCS, enabling communication between controllers, field devices, and HMIs. Common protocols used include Ethernet, Profibus, and Fieldbus.
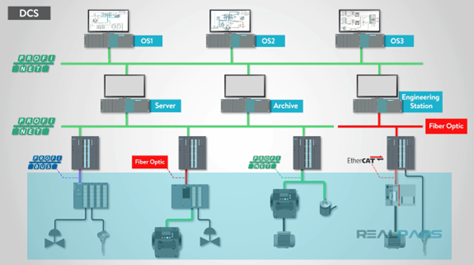
- Key Features of DCS:
- Decentralized Control: Control functions are distributed across multiple controllers, each responsible for a specific part of the process.
- Scalability: DCS systems can easily scale to accommodate new controllers or processes as the plant expands.
- Redundancy: DCS systems often include redundant controllers and communication paths to ensure reliability and uptime.
- Integration: DCS systems are designed to integrate with various automation systems, sensors, and actuators within the plant.
- Applications of DCS:
- Process Industries: DCS is widely used in industries like oil and gas, chemical processing, power generation, and water treatment, where complex processes need to be managed and controlled.
- Large-Scale Operations: DCS is ideal for large-scale operations where centralizing control would be impractical.
- Benefits of DCS:
- Improved Process Control: DCS allows for precise control of complex processes, leading to increased efficiency and product quality.
- Enhanced Reliability: With distributed control and redundancy, DCS systems are highly reliable and reduce the risk of plant-wide failures.
- Centralized Monitoring: Even though control is distributed, operators can monitor and manage the entire process from a central HMI.
- Flexibility: DCS systems can be easily adapted to changes in process requirements or expansions in the plant.

