What is an HMI System?
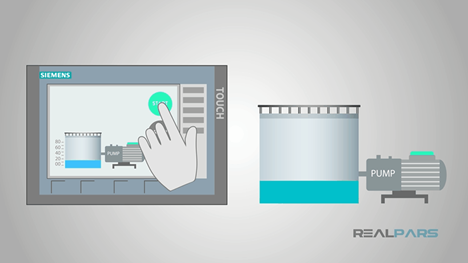
A Human-Machine Interface (HMI) is a user interface that allows humans to interact with machines, systems, or devices. In the context of industrial automation, HMI systems are crucial as they provide operators with a graphical interface to monitor, control, and manage machines and processes. These systems are typically found in industries such as manufacturing, energy, water treatment, and transportation.

2. Key Components of HMI Systems:
- Display Interface: The HMI display, usually a touch screen or a computer monitor, shows real-time data, process status, and controls. It visualizes data in the form of charts, graphs, alarms, and controls.
- Control Panels: HMIs often include control panels where operators can start, stop, and adjust various parameters of the machinery or processes they manage.
- Communication Interface: HMIs communicate with Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), sensors, and other automation devices through communication protocols like Ethernet, Modbus, or Profibus.

3. Functions of HMI Systems:
- Monitoring: Operators can monitor real-time data such as temperature, pressure, flow rates, and production levels.
- Control: HMI systems allow operators to control processes and machinery by sending commands to PLCs and other automation systems.
- Alarm Management: HMIs can display alarms when a process deviates from normal operating conditions, allowing operators to take corrective actions.
- Data Logging and Reporting: HMIs can log process data and generate reports for analysis and troubleshooting.

- Benefits of HMI Systems:
- User-Friendly Interface: Provides an intuitive and easy-to-use interface for operators.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Allows for real-time visibility into processes, enabling quick decision-making.
- Improved Efficiency: Streamlines operations by providing centralized control and monitoring.
- Reduced Downtime: With effective alarm management and real-time monitoring, potential issues can be identified and resolved quickly.